
Customized Security for AI
Disclaimer: The thoughts and ideas presented in this course are not to be substituted for legal or ethical advice and are only meant to give you a starting point for gathering information about AI policy and regulations to consider.
Learning objectives:
- Understand the motivation behind customized security needs for AI tools
- Discuss a variety of low to high investment strategies for meeting customized security needs
- Define and be able to contrast the differences between secure AI services, deidentifying data, and deploying existing models on secure computing resources.
Intro
Customized security needs are perhaps one of the largest barriers keeping individuals in certain fields from using AI tools to their full potential. There are many legitimate reasons commercial AI tools cannot and should not be used with protected data.
Commercial AI products do not have data use agreements. They do not have to tell you what they do with your data. And if you work with protected data types that generally means you can’t use them.

Not all data types are safe to share for a variety of reasons. To protect patients or customers, Personal Identifiable Information (PII) Protected Health Information (PHI) cannot be used with online AI services or shared with others. Controlled Unclassified Information is another type of protected data that may be related to national security matters.
But protected data projects could highly benefit from AI!

- AI analysis tools as helpful diagnostic aids for use with health data, imaging data, genomic data.
- AI chatbots as an aid for financial or health guidance for patients or customers.
- AI to help detect when protected data has been leaked.
Protected data might be useful as training data for a problem and/or patients or customers may want to input data into a secure AI tool.

- Protected data needs should always be taken seriously! Before employing any AI solutions that involve protected data consult your legal experts and IRB!
Data security basics
Before we dive into AI related solutions, it’s a good idea that we remind ourselves of some of the best practices for data privacy

- Fewest individuals have access to the data as possible
- Least privileges as needed to complete a task. This is known as the “principles of least privilege”.
- Individuals who do have access should have to provide authentication to make sure only authorized individuals can see the data.
- Data use agreements need to be used when individuals need to be added to the authorized list
Secure AI solutions for protected data
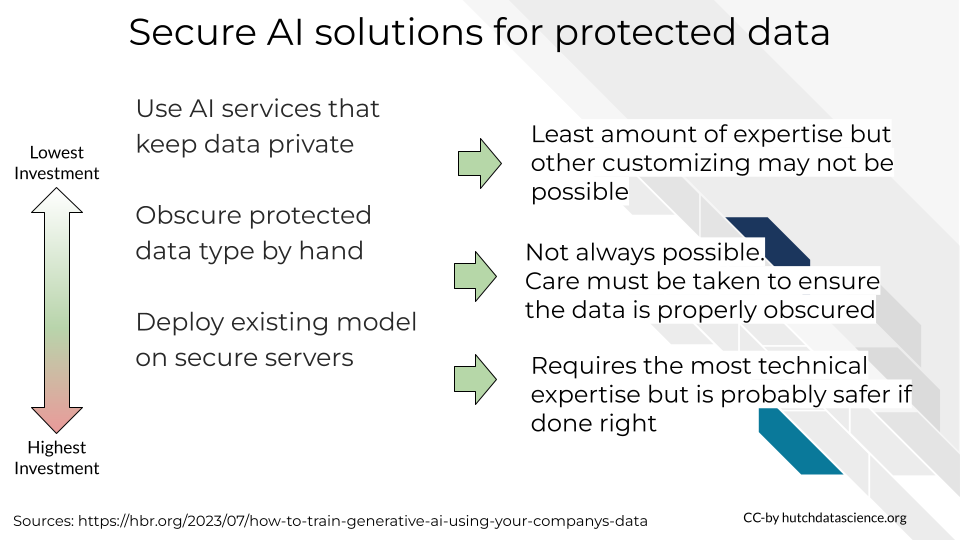
Solutions exist for AI tools for protected data – some require more careful planning thought and expertise. Here we have ordered these example strategies in order of least to most investment.
 Whenever possible consult data security and legal experts to be sure that you are not exposing patients or customers’ data and risking their privacy or finances.
Whenever possible consult data security and legal experts to be sure that you are not exposing patients or customers’ data and risking their privacy or finances.
- Use AI services that keep data private – some AI tools have specialized tools that allow you to keep data private. Be sure to carefully read their terms of use to gain an understanding of how they keep the data secure. Consult security
- Obscure protected data type by hand and use AI models. In some cases this is not possible to do and still have meaningful data. And, care must be taken to make sure that data it thoroughly and properly secured.
- Deploy existing model on secure servers. This takes the most technical expertise to carry out.
Data obscuring techniques
Whether you have an AI service perform this or you do it yourself (or both) there are multiple strategies for obscuring data. It is often not a bad idea to employ multiple safety nets to keep data safe.
In summary, here’s just a few of the techniques that can help make data sharing HIPAA compliant.

- Data Aggregation - summarize values to a higher level of grouping
- Data Masking - Replace data with symbols
- Data Anonymization - Replace data with randomized, fake data.
- Data Redaction - Remove the sensitive data
To further understand what this looks like, here’s an example of how these techniques might look with a toy dataset
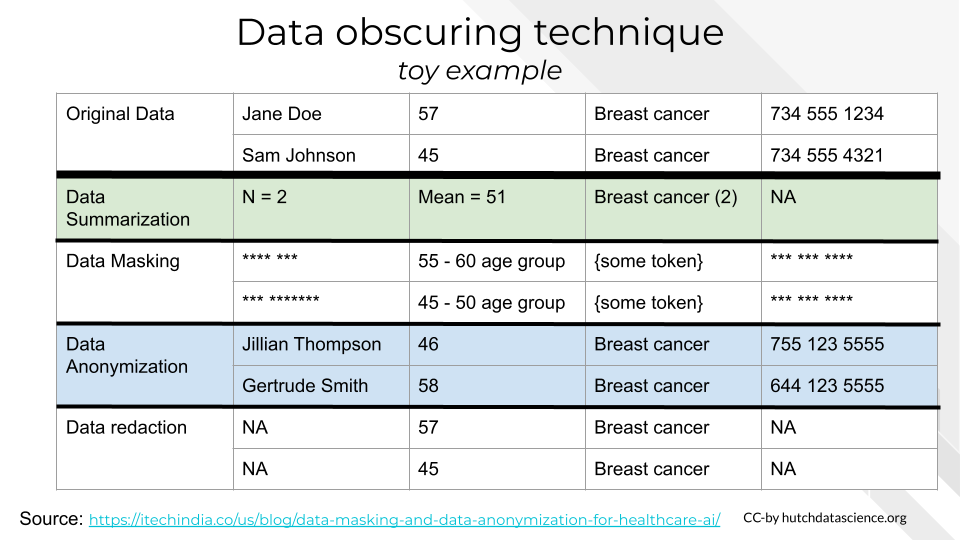
In this toy example will illustrate roughly how a given technique may obscure the original data in the top row. This can give you a sense that some types of data are better for certain types of obscuring methods than others. But this also depends on what your goals for your AI project are.
Keep in mind that data anonymization may be more difficult with smaller datasets because of a concept called K anonymity. This principles means that you need to make sure that k number of individuals share the same attributes so that it is nearly impossible to identify any specific subject.
The strategy you choose should definitely include these two questions:

- What protected items are included in your data
- Your goals with said data with AI – what is the minimum amount of information you could include in the AI model or input in order to achieve the desired goals?
Example Security Customization strategies
In the table below we show three examples illustrating example strategies for using AI tools with protected data. These examples are in the order of least to most amount of technical expertise needed to implement.

PrivateAI
PrivateAI is a platform that allows you to use various AI models with private data. It works by detecting and redacting information that is likely protected like PII and PHI. It also has containerization options that allow you to run AI but not on their or other’s servers. It requires the least technical expertise to implement, but care must be taken to make sure that it will properly deal with your project’s particular type of protected data.
deidentify
deidentify is a Python package that can assist with deidentifying medical records using natural language programming. This is illustrative of one way you might attempt to deidentify data before using it with AI tools. Care must be taken to make sure that the deidentification process is thorough. You may also want to couple this with other tools that can detect PII or PHI data before you submit to an AI tool. As always you will want to make sure that it properly handles your project’s data and that before you submit the data you’ve deidentified you have other reputable sources double or triple check that no protected information is being leaked.
AWS servers + HuggingFace
Amazon web services (and its competitors) generally offer HIPAA compliant computing solutions. Whether you use this service, an institutional cluster, or some other server is a decision you will have to make on a case by case basis. But regardless, this is the most technically involved solution. This is most likely the strategy you’d need to employ if security is not your only customization you need. In this instance you would borrow a model and set up from HuggingFace and build your AI tool more or less from scratch (but don’t build the model from scratch)
Always double, triple, quadruple, check
As opposed to other types of AI customizations, the strategies we’ve discussed in this chapter are the most imperative that you get cleared through the proper channels before deploying (if you do this incorrectly it may be illegal). It is a matter of privacy and safety for patients/customers that you get this right. So it makes sent to check with your in-house experts like institutional review boards and data security experts!

–>