
Chapter 11 RNA Methods
This chapter is in a beta stage. If you wish to contribute, please go to this form or our GitHub page.
11.1 Learning Objectives

11.2 What are the goals of gene expression analysis?
The goal of gene expression analysis is to quantify RNAs across the genome. This can signify the extent to which various RNAs are being transcribed in a particular cell. This can be informative for what kinds of activity a cell is undergoing and responding to.
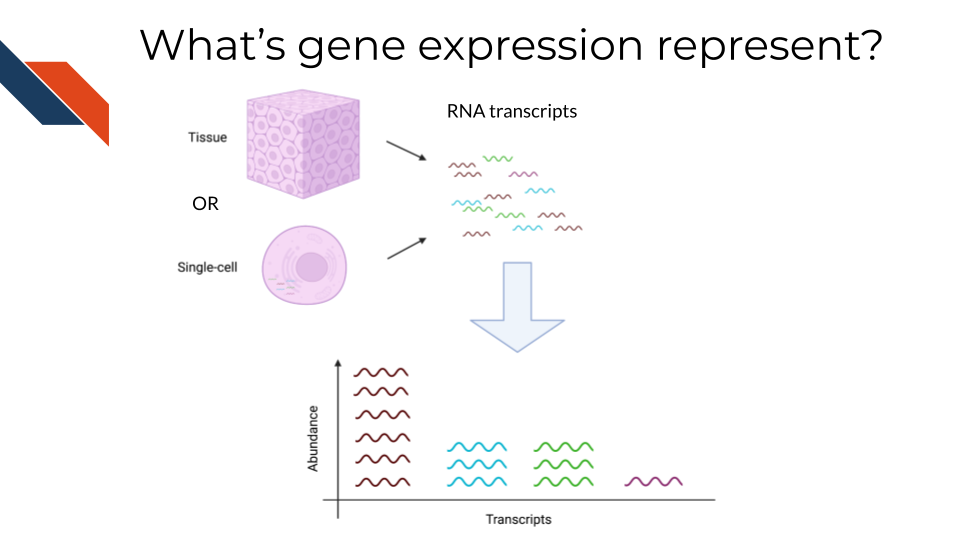
11.3 Comparison of RNA methods
There are three general methods we will discuss for evaluating gene expression. RNA sequencing (whether bulk or single-cell) allows you to catch more targets than gene expression microarrays but is much more costly and computationally intensive. Gene expression microarrays have a lower dynamic range than RNA-seq generally but are much more cost effective.
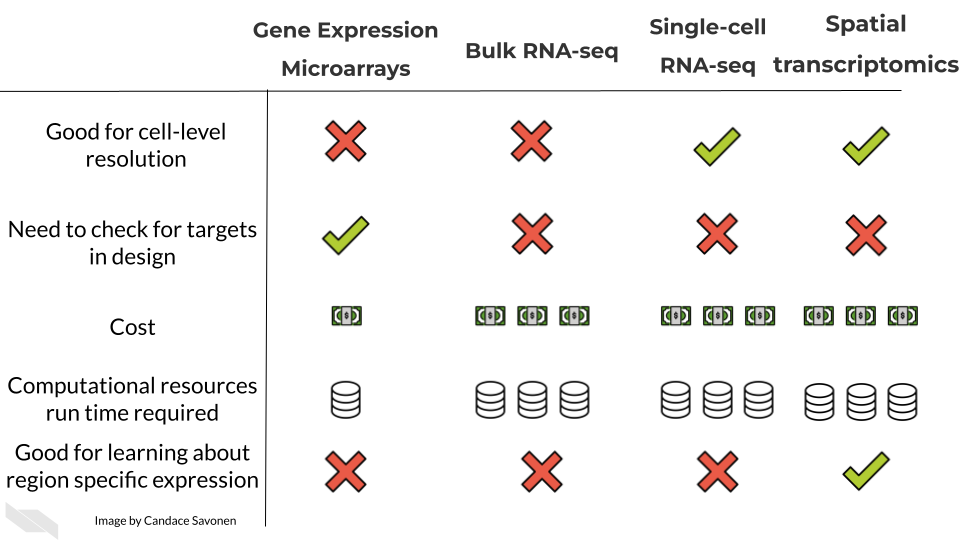
In these upcoming chapters we will discuss in more detail each of these methods, what the data represent, what you need to consider, and what resources you can consult for analyzing your data.