Cognitive Psychology
How we process tables
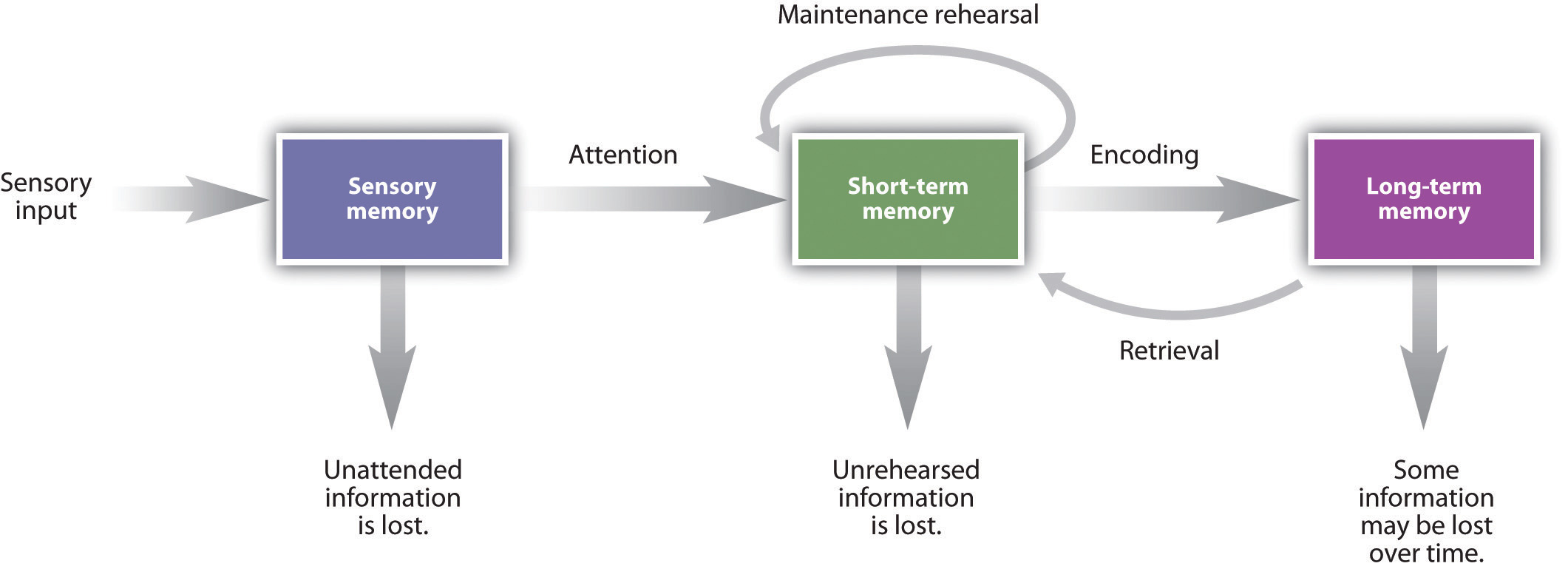 https://opentextbc.ca/introductiontopsychology/chapter/8-1-memories-as-types-and-stages/
https://opentextbc.ca/introductiontopsychology/chapter/8-1-memories-as-types-and-stages/
- Sensory memory
- Retains visual input for ~1/2 second
- Memory without understanding
- Where we can use visual (preattentive) attributes to highlight
- Working memory
- Can only hold (+/-) 5 elements at once
- Too many elements
- Make it easier by grouping elements
Principles of Table Reading
Tables are not tidy data in general!
- Directionality
- Grouping
- Highlighting
- Precision
Directionality / Structure
- Think about groupings / categories in data
- Use columns for a category if you
- want to compare values across categories
- In general, the conventions are
- Read Right to Left
- Read Up to Down
Table Directions
- Unidirectional - only meant to be read in one direction
- categorical values can be organized by row or column, but not both
- Marginals in only one direction
- Bidirectional
- categorical values arrange by both row and column
- Marginals in both directions
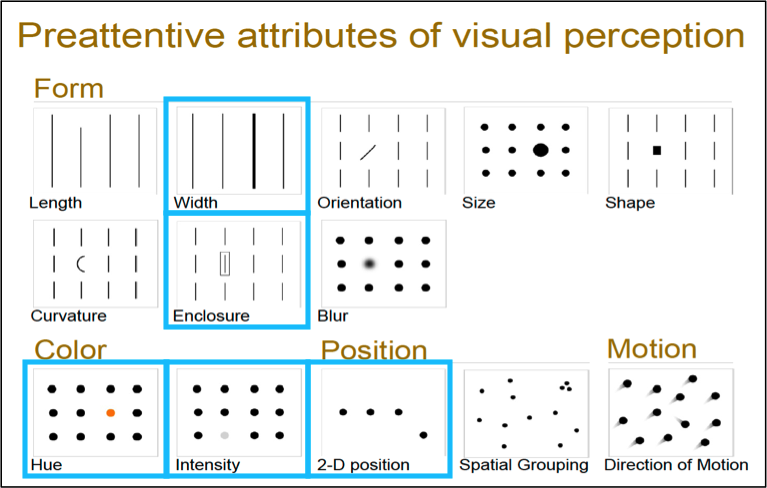
Preattentive Attributes
How you get the attention at the Sensory memory level - we immediately process this kind of information:
- Form
- Length (quantitative)
- Width (quantitative)
- Orientation
- Size (limited quantitative)
- Enclosure
- Color
- Hue
- Intensity (quantitative)
- Spatial Position
- 2-D position (quant)
The Brain can process at most 1 pretattentive attribute
- “Pre-attentive symbols become less distinct as the variety of characters (hues, etc) increases” (Ware)
- “The immediacy of any preattentive cue declines as the variety of alternative patterns increases, even if the patterns are visually distinct”
- Runs into limitations of working memory
- 8 distinct colors
- 4 orientations
- Runs into limitations of working memory
Gestalt Principles
- How do we help people decide whether something is part of a group?
- Perception principles for signalling
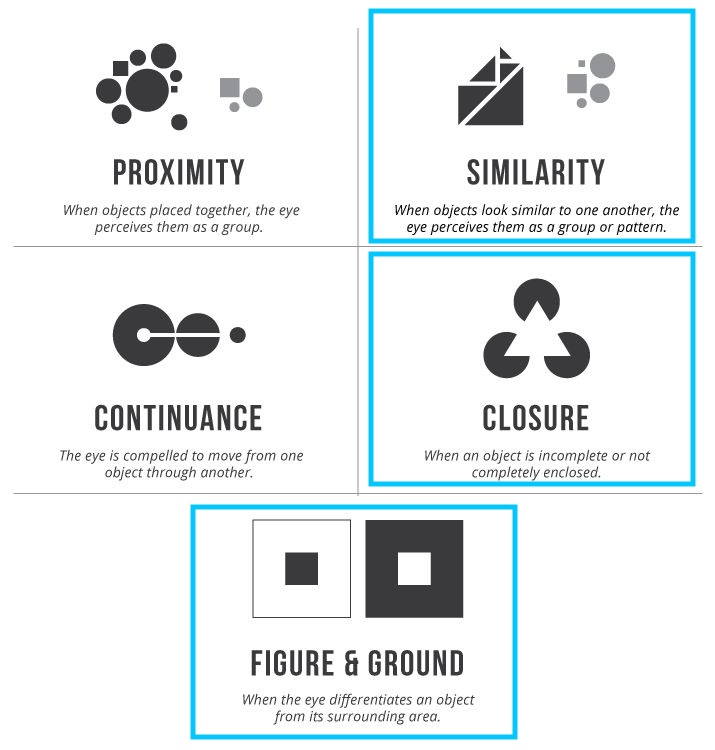 https://design4users.com/gestalt-theory-for-ux-designers-principle-of-similarity/
https://design4users.com/gestalt-theory-for-ux-designers-principle-of-similarity/
References
- [Show me the Numbers]
- https://nwc.design/the-science-of-infographic-design/