Chapter 10 Creating handy reference guides

10.1 The goal of a reference guide
Reference guides are the dictionary of your tool: they aren’t meant to be read front to back, but the best ones are easily searchable. Your user will have something in mind that they are trying to find information on – the quicker they can find it, the quicker their question can be answered.
Our goal for a reference guide is to be as comprehensive, navigable, and as always, as clear as possible.
10.2 Characteristics of handy reference guides
10.2.1 Is easy to find
As with our other documentation sections, no matter how well they are crafted, they are of no use if no one can find them. Make sure that a link to the reference guide is clear to find in a navigation bar and/or the main page.
If the reference guide is a part of a command line package, make sure that it is clear in your documentation what command you need to see it (e.g. --help).
10.2.2 Is searchable
Users will be digging into your reference guide looking for a specific entry. Making your reference guide alphabetical is a start. If you are able to make terms searchable that’s even better, but at the very least, if your reference guide is visually easy to be scan, that can serve a similar function.
10.2.3 Is comprehensive
All items are covered in the reference guide – every. single. thing. This includes all:
- Terms
- Functions
- Arguments
- Parameters
- Defaults
- Datasets or items included in the package
- Buttons (in the case of a GUI)
The most useful entries in these reference guides…
- Not only define the item, but tell how it relates to other items (and they have links where relevant).
- Discuss all the possible inputs that can be used as well as how to decide which input fits the user’s needs.
- Make any existing defaults very clear.
- Shows the usage of that item in context – some example lines of code go a long way.
- Tries to avoid the use of jargon, but if it is absolutely necessary to use a jargon-y term it links to information about the meaning of the term.
Take a look at DESeq2’s reference guide, (Love2014?) do a great job at their entries – covering the right amounts of information and informing the user about how to decide what works for them.
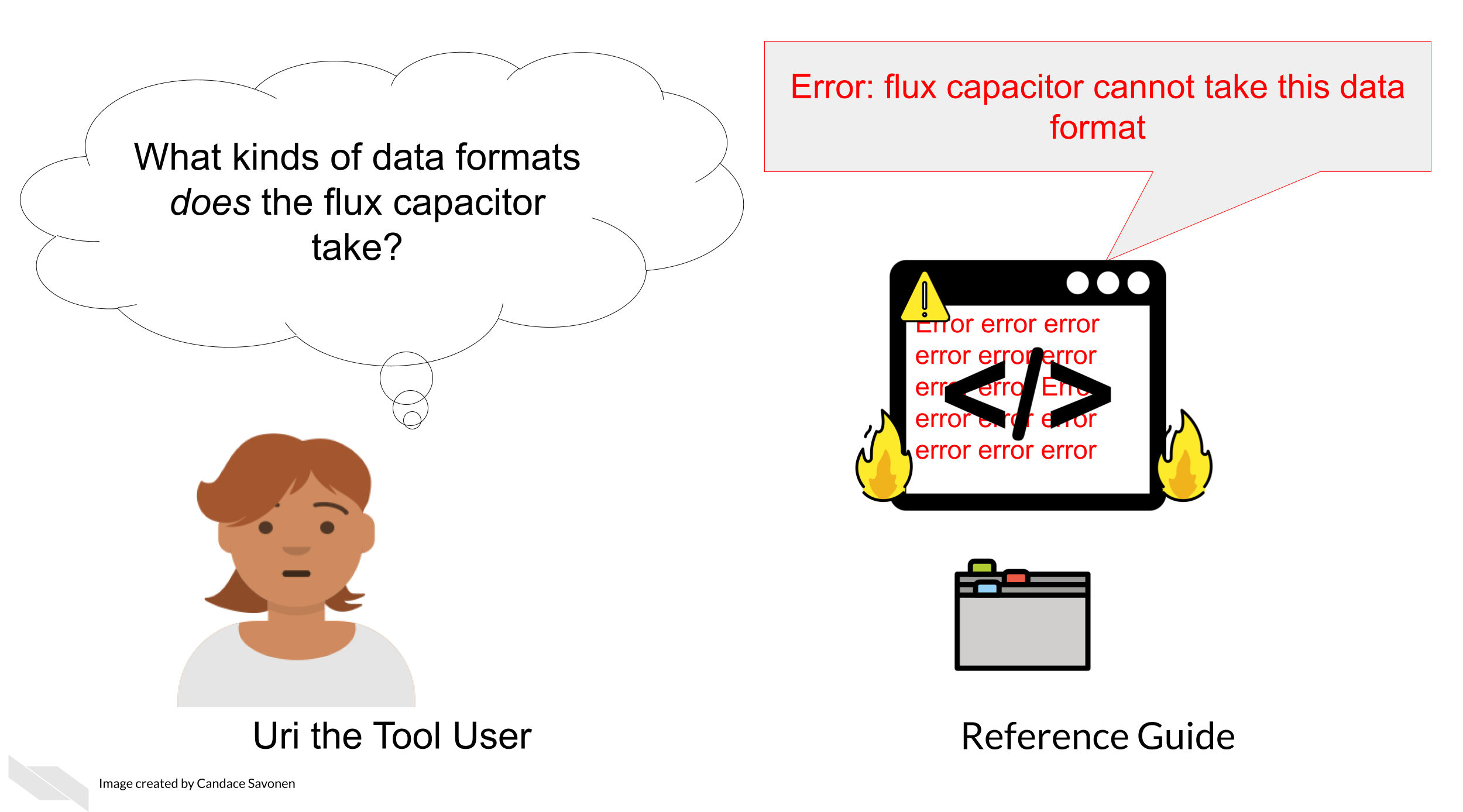
10.2.4 Data formats are described
Perhaps after installation, getting data formatted correctly is one of the other very large hurdles users will need to deal with.
Ideally, your tool can use a data format that is common. But the more that your tool is particular about an odd data format, the more your documentation needs to be specific about what the odd data format looks like.
- Include example files for a positive control/example.
- Send your user to any tools they can use to convert their data format automatically.
- If its feasible, include an automatic data converter as a part of your tool.
GSEA has great descriptions of their data formats with examples of what the data formats look like.
10.2.5 Entries should have a consistent format
Consistency helps your users know what to expect and know where to find information! Each entry in the reference guide should have the same format and sections, in the same order.
Depending on the destination of your package, a consistent format may already be determined for you. Bioconductor packages have specific guidance on these reference manuals.
To recap:

10.3 Good examples of reference guides
QIIME2 has a great reference guide! (Bolyen2019?) cover all items and terms with lots of links to more information or related entries.
Bioconductor packages have a consistent reference guide format that the packages there adhere to which makes it easier for users to find what they are looking for once they are familiar with the format. A typical package’s reference guide looks like this.
10.4 Exercise: Create your own reference guide!
For R package documentation: Follow the advice from Hadley Wickham from the R Packages book which includes using roxygen2 package to automatically render those .Rd files!
If your tool’s destination is Bioconductor, see their specific guidance on manual pages.
For Python package documentation:
Follow the docstrings guidance and instructions here.
For other general purposes, you can our the reference guide template to start your own reference guide either by using the markdown template directly, or navigating to the MkDocs repository you set up in the previous chapter.
10.5 How to keep your documentation up to date

10.5.1 The goal of documentation maintenance
Perhaps you’ve been making improvements or otherwise updating your software tool. That’s excellent and you deserve a big kudos for continuing maintenance on your tool!
But your work is not done yet. For each (user-facing) update you make to the tool, you should also make a documentation update. As a user, the only thing worse than having a tool with no documentation at all is having a tool with documentation that is out of date or otherwise incorrect.
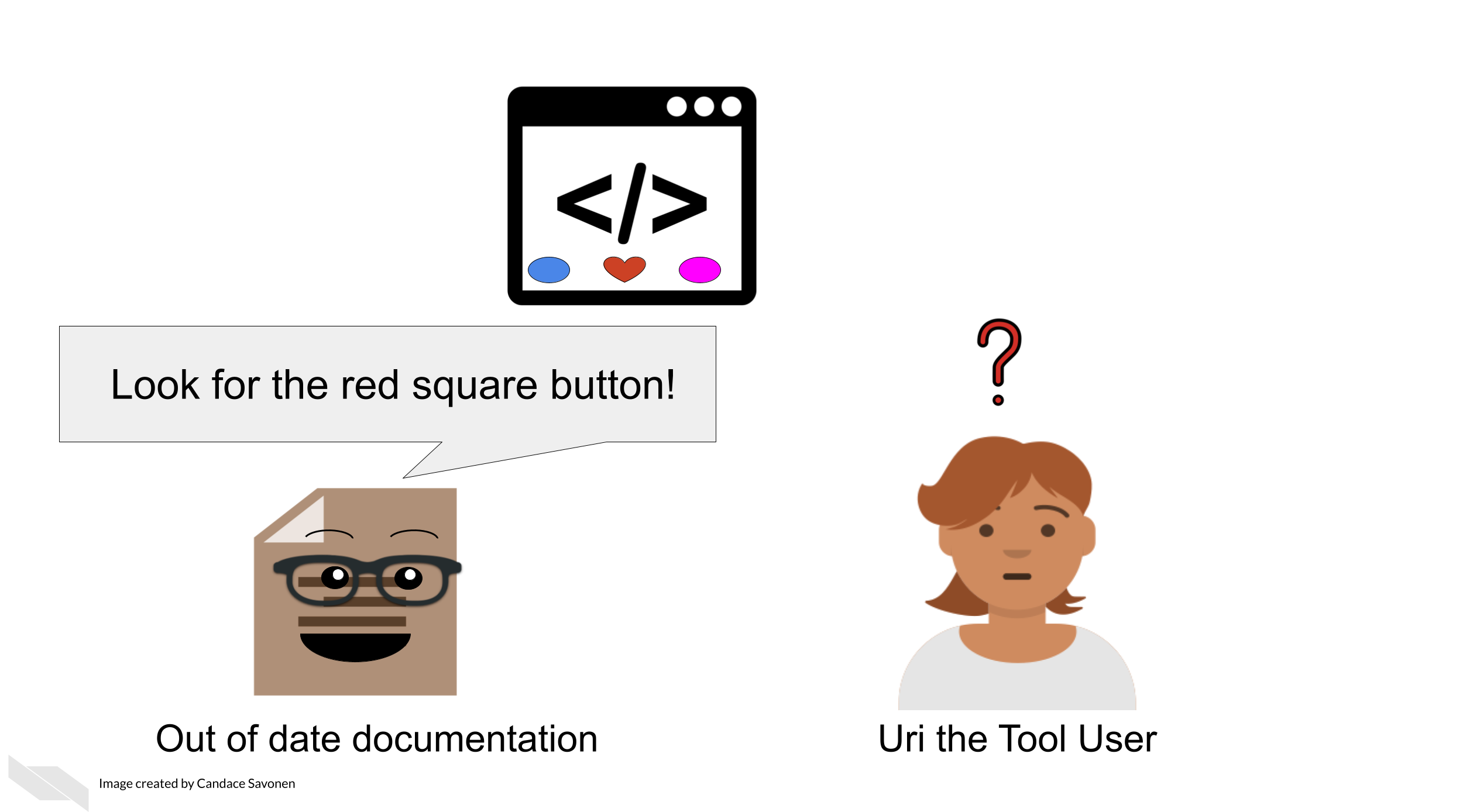
If documentation updates aren’t prioritized, your tool can easily get several versions ahead leaving the documentation you carefully crafted rather useless and misleading.
10.5.2 Keep your documentation in one, version-controlled place
Presumably you have some sort of process for version controlling your tool updates (we assume GitHub but could be other services). Ideally, your documentation should be version controlled similarly and, if appropriate, in the same place. The easier you make it on yourself to update your documentation, the more likely future you will be at updating it successfully! It’s worth spending time thinking about your own development process and how you can make it easier on yourself and your team for longer-term better maintained documentation.
10.5.3 Do not consider a tool fix done before its relevant documentation update is also completed
However you track your tasks, also track your documentation issues and always pair a software fix with a documentation fix – or at least check if it affects anything user-facing. To help you remind you of this, you may want to use an issue template (if you use GitHub) and make sure that issue template includes a reminder to update documentation.
10.5.4 Make sure links work
A very simple but all too common problem with out of date documentation is broken links!
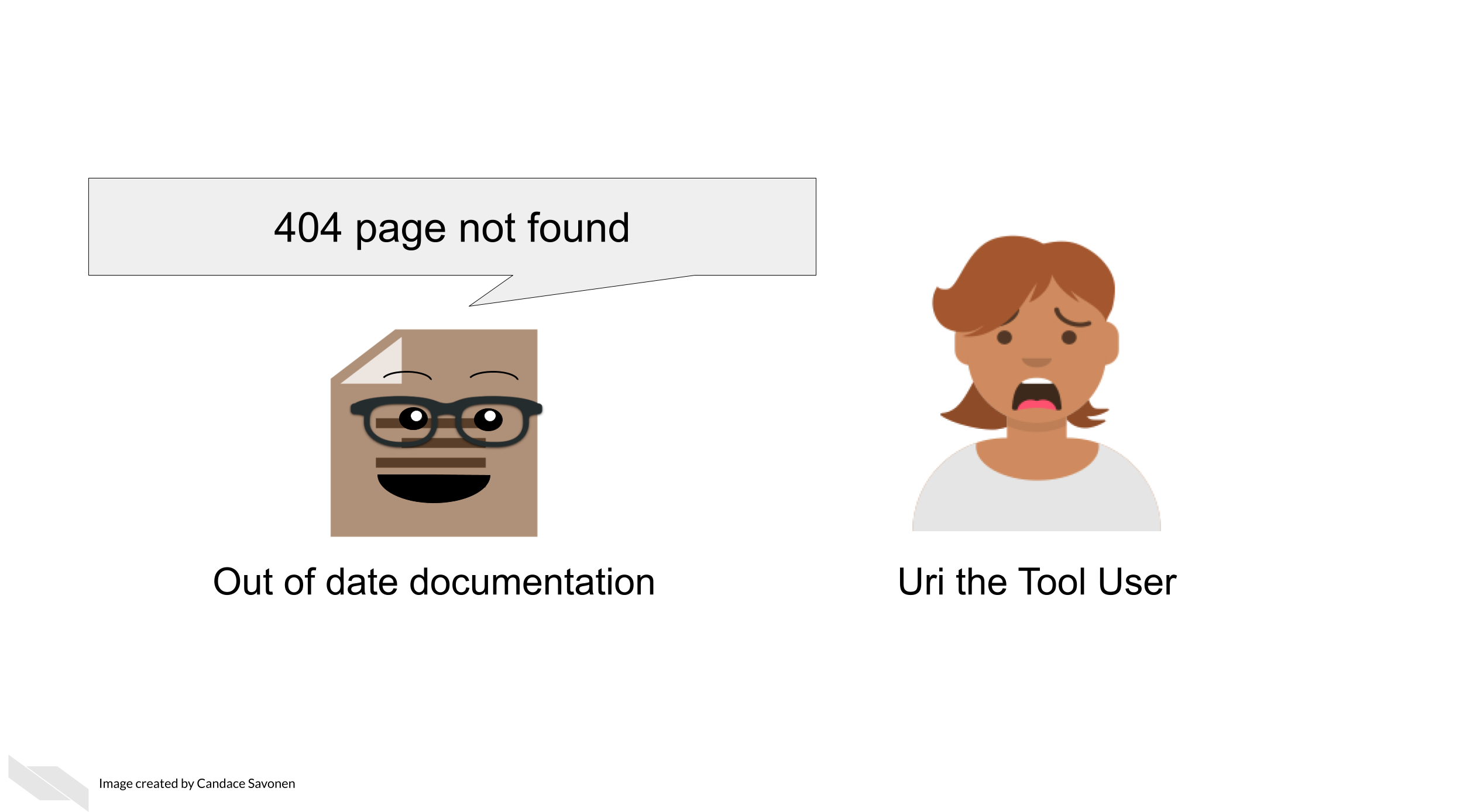
You can catch these broken links by manually clicking on all your links, but sometimes broken links will still slip through the cracks anyway! There are GitHub actions and other automated tools that can check your URLs for you. Take advantage of automation to do this for you so you can save your time an effort for other improvements to your tool and documentation!
Here’s some options for automated URL-checking:
10.6 Exercise 1: Add a reminder for documentation updates to your task manager
- If you use GitHub, add an issue template that has a reminder to update documentation.
- If you use something else for task management, look for some other way to remind yourself (and your fellow developers on the project) to keep documentation up-to-date for each change.
10.7 Exercise 2: Implement a URL checker
- If you use GitHub for your documentation, add a url checking GitHub action to your repository.
We used a url-checker GitHub action for developing this course!
You can see ours here for an example.
- If you use something else for version control, look into URL checkers that you can easily implement into your development process.
Disclaimer: The thoughts and ideas presented in this course are not official NIH guidance and are not a substituted for legal or ethical advice and are only meant to give you a starting point for gathering information data management.
For all cartoons:
Avataars by https://getavataaars.com/.
Icons by https://thenounproject.com/ License CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
Emojis by OpenMoji License: CC BY-SA 4.0.↩︎