Introduction

Motivation
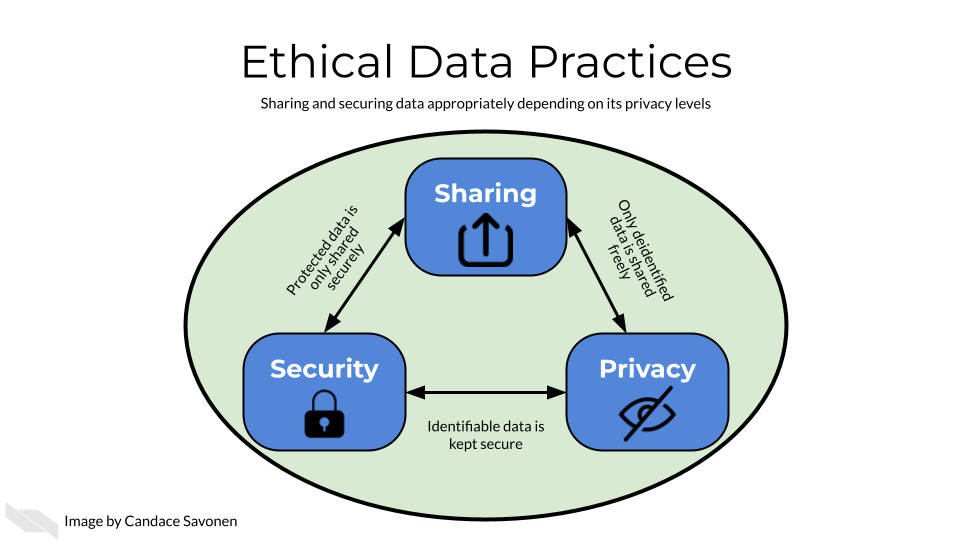
One of the key cancer informatics challenges is dealing with and managing the explosion of data from multiple sources. This course is designed to help researchers and investigators to understand the key ethical principles of data management from a privacy, security, usability and discoverability perspective.
Target Audience
This course is intended for researchers (including postdocs and students) with limited to intermediate experience with informatics research. The conceptual material will also be useful for those in management roles who are collecting data and using informatics pipelines.

Topics Covered
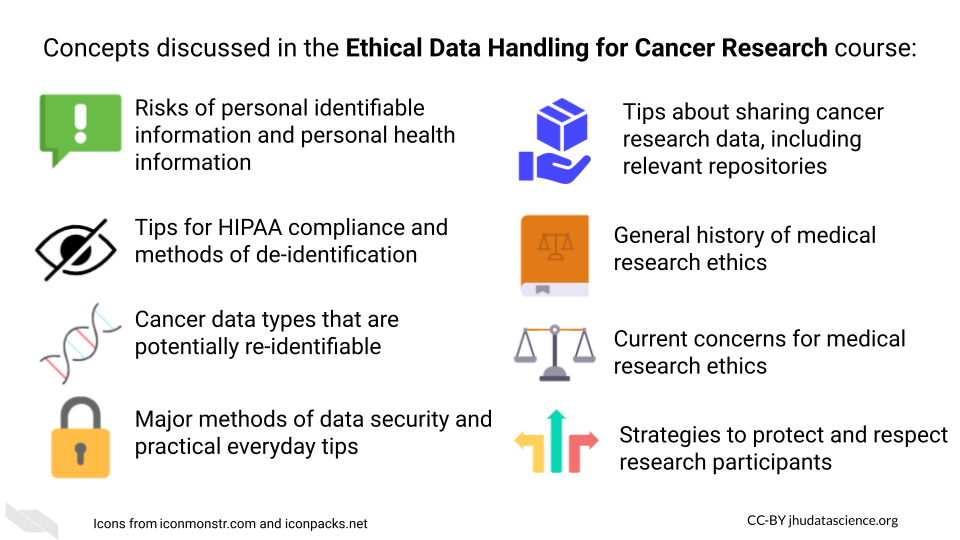
Curriculum
The course will cover key underlying principles and concepts in ethical data handling.

It will also cover how best practices for data security, data privacy, and data sharing are critical for responsible data management.